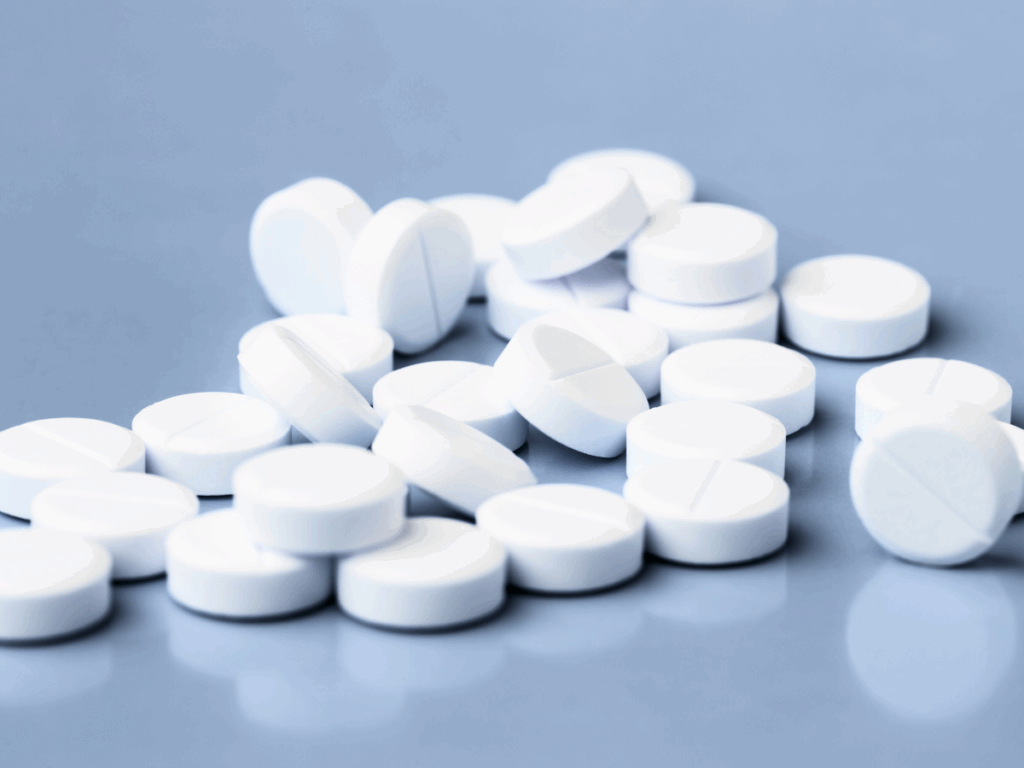

What Are Amphetamines?
Amphetamines are powerful central nervous system stimulants used in both medical and illicit settings. Medically, they are prescribed to treat conditions such as ADHD, narcolepsy, and sometimes obesity. However, due to their euphoric effects and ability to increase energy and focus, amphetamines are often misused, leading to a high potential for abuse and addiction.
Recognizing Amphetamine Dependence and Addiction
Amphetamine misuse falls under the clinical diagnosis of Stimulant Use Disorder (SUD), a condition marked by the persistent, compulsive use of stimulants despite clear harm. This pattern often disrupts mental, emotional, and relational stability, impacting decision-making, personal responsibilities, and overall well-being. Early signs may include escalating use, preoccupation with obtaining or taking the drug, and difficulty functioning without it. Recognizing these shifts with honesty and compassion is the first step toward meaningful, restorative care.
What Makes Amphetamines Addictive?
Amphetamines are addictive because they increase levels of dopamine, norepinephrine, and serotonin in the brain—chemicals that regulate mood, energy, and pleasure. This chemical surge results in euphoric effects that users often seek repeatedly, reinforcing use and escalating into dependence.
Biological Factors
- Repeated amphetamine use leads to neuroadaptation, where the brain reduces its natural production of dopamine and becomes reliant on the drug.
- Genetic predisposition and pre-existing mental health conditions may increase the risk of developing addiction.
Psychological Factors
- People often use amphetamines to cope with emotional pain, trauma, stress, or untreated mental health disorders.
- Social pressures and environments that normalize drug use can also contribute to psychological dependence.
How Do Amphetamines Affect the Brain?
Amphetamines significantly alter brain chemistry by overstimulating neurotransmitter systems, especially dopamine. This leads to intense emotional highs followed by severe crashes, disrupting natural mood regulation. Over time, the brain’s ability to function without the drug deteriorates.
Short / Long-Term Effects on the Brain
- Short-Term: Heightened alertness, increased focus, improved mood, but also anxiety and agitation.
- Long-Term: Cognitive decline, memory loss, poor decision-making, and the risk of amphetamine-induced psychosis.
How Do Amphetamines Affect the Body?
Physically, amphetamines elevate heart rate and blood pressure and suppress appetite, putting extreme strain on the cardiovascular and metabolic systems. Long-term use can result in serious, sometimes irreversible, damage to physical health.
Short / Long-Term Effects on Body
- Short-Term: Euphoria, increased energy, dilated pupils, reduced appetite, insomnia.
- Long-Term: Cardiovascular disease, severe weight loss, malnutrition, dental decay (“meth mouth”), skin sores, and infections.
Overdose Risk
Amphetamine overdose can be life-threatening and may lead to seizures, stroke, heart attack, or death. The risk is heightened when amphetamines are used in combination with other substances or at high doses over time.
Amphetamine Withdrawal Symptoms
When a person stops using amphetamines after prolonged use, they often face intense physical and emotional symptoms. These include fatigue, depression, sleep disturbances, irritability, and strong cravings.
Treatment Programs for Amphetamine Addiction
Successful recovery from amphetamine addiction typically begins with medically supervised detox, followed by behavioral therapies and support systems. Inpatient programs offer a structured environment, while outpatient options provide flexibility for milder cases. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT), motivational interviewing, and contingency management are among the most effective approaches.
Support groups like SMART Recovery and Narcotics Anonymous also play a vital role in maintaining sobriety. While no medications are FDA-approved specifically for amphetamine addiction, antidepressants and other supportive drugs may be used to ease withdrawal symptoms and stabilize mood. Legacy Healing Center provides comprehensive, compassionate care tailored to each individual’s needs, guiding them through detox and toward lasting recovery.
Step Into a Life Beyond Amphetamines
If you or someone you love is caught in the cycle of amphetamine use or facing the challenges of withdrawal, you don’t have to face it alone. Compassionate, expert care is always within reach. Our team is available 24/7 at (888) 534-2295 to guide you toward safe, personalized treatment, including medically supervised detox, psychiatric support, and long-term recovery planning tailored to your individual needs.
Not sure where to begin? You can verify your insurance securely online or speak directly with a knowledgeable specialist. We’ll walk you through your options and connect you with trusted resources designed to bring clarity, peace of mind, and a renewed sense of direction.
Reaching out is more than a decision—it’s a turning point. When you’re ready to leave behind the chaos of stimulant use and reclaim a life of focus, vitality, and purpose, we’ll be here to walk beside you every step of the way.
Immediate Help and Support
Whether you’re preparing for treatment or just starting to ask questions, these confidential resources are available:
- Legacy Healing Center: Call (888) 534-2295 to speak confidentially with a specialist in amphetamine and stimulant addiction.
- SAMHSA National Helpline: Dial 1‑800‑662‑HELP (4357) for 24/7 support and treatment referrals.
- 988 Suicide & Crisis Lifeline: Dial 988 for immediate assistance during a mental health or substance-related crisis.
You are not alone. Support is closer than you think.


 Written By:
Written By: Edited By:
Edited By: Clinically Reviewed By:
Clinically Reviewed By: 



 Verify Insurance
Verify Insurance